The ScaledTorsSimpleCo class describes an scaled torsion internal coordinate of a molecule. More...
#include <simple.h>
Inheritance diagram for sc::ScaledTorsSimpleCo:
Collaboration diagram for sc::ScaledTorsSimpleCo:
Public Member Functions | |
| ScaledTorsSimpleCo (const ScaledTorsSimpleCo &) | |
| ScaledTorsSimpleCo (const char *refr, int, int, int, int) | |
| This constructor takes a string containing a label, and four integers a, b, c, and d which give the indices of the atoms involved in the torsion angle abcd. More... | |
| ScaledTorsSimpleCo (const Ref< KeyVal > &) | |
| The KeyVal constructor. More... | |
| const char * | ctype () const |
| Always returns the string "TORS". | |
| double | radians () const |
| Returns the value of the angle abc in radians. | |
| double | degrees () const |
| Returns the value of the angle abc in degrees. | |
| double | preferred_value () const |
| Returns the value of the angle abc in degrees. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SimpleCo Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SimpleCo | |
| SimpleCo (int, const char *=0) | |
| This constructor takes an integer argument which is the number of atoms needed to describe the coordinate. More... | |
| SimpleCo (const Ref< KeyVal > &, int natom) | |
| The KeyVal constructor requires the number of atoms. | |
| int | natoms () const |
| Returns the number of atoms in the coordinate. | |
| int | operator[] (int i) const |
| Returns the index of the i'th atom in the coordinate. | |
| void | save_data_state (StateOut &) |
| Save the base classes (with save_data_state) and the members in the same order that the StateIn CTOR initializes them. More... | |
| SimpleCo (StateIn &) | |
| virtual int | operator== (SimpleCo &) |
| int | operator!= (SimpleCo &u) |
| double | force_constant (Ref< Molecule > &) |
| Returns an approximate force constant (a la Almlof). | |
| void | update_value (const Ref< Molecule > &) |
| Recalculates the value of the coordinate based on the geometry in the Molecule. | |
| void | bmat (const Ref< Molecule > &, RefSCVector &bmat, double coef=1.0) |
| Fill in a row of the B matrix. | |
| virtual double | calc_force_con (Molecule &)=0 |
| Calculates an approximate force constant and returns it's value. | |
| virtual double | calc_intco (Molecule &, double *=0, double=1)=0 |
| Calculate the value of the coordinate based on what's in Molecule. More... | |
| void | print_details (const Ref< Molecule > &, std::ostream &=ExEnv::out0()) const |
| Print the coordinate. | |
| int | equivalent (Ref< IntCoor > &) |
| Tests to see if two coordinates are equivalent to each other. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::IntCoor Public Member Functions inherited from sc::IntCoor | |
| IntCoor (StateIn &) | |
| IntCoor (const IntCoor &) | |
| IntCoor (const char *label=0) | |
| This constructor takes a string containing a label for the internal coordinate. More... | |
| IntCoor (const Ref< KeyVal > &) | |
| The KeyVal constructor. More... | |
| virtual const char * | label () const |
| Returns the string containing the label for the internal coordinate. | |
| virtual double | value () const |
| Returns the value of the coordinate in atomic units or radians. | |
| virtual void | set_value (double) |
| Sets the value of the coordinate in atomic units or radians. | |
| virtual void | print (std::ostream &o=ExEnv::out0()) const |
| Print information about the coordinate. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState | |
| SavableState & | operator= (const SavableState &) |
| void | save_state (StateOut &) |
| Save the state of the object as specified by the StateOut object. More... | |
| void | save_object_state (StateOut &) |
| This can be used for saving state when the exact type of the object is known for both the save and the restore. More... | |
| virtual void | save_vbase_state (StateOut &) |
| Save the virtual bases for the object. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::DescribedClass Public Member Functions inherited from sc::DescribedClass | |
| DescribedClass (const DescribedClass &) | |
| DescribedClass & | operator= (const DescribedClass &) |
| ClassDesc * | class_desc () const throw () |
| This returns the unique pointer to the ClassDesc corresponding to the given type_info object. More... | |
| const char * | class_name () const |
| Return the name of the object's exact type. | |
| int | class_version () const |
| Return the version of the class. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount Public Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount | |
| int | lock_ptr () const |
| Lock this object. | |
| int | unlock_ptr () const |
| Unlock this object. | |
| void | use_locks (bool inVal) |
| start and stop using locks on this object | |
| refcount_t | nreference () const |
| Return the reference count. | |
| refcount_t | reference () |
| Increment the reference count and return the new count. | |
| refcount_t | dereference () |
| Decrement the reference count and return the new count. | |
| int | managed () const |
| void | unmanage () |
| Turn off the reference counting mechanism for this object. More... | |
| int | managed () const |
| Return 1 if the object is managed. Otherwise return 0. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::Identity Public Member Functions inherited from sc::Identity | |
| Identifier | identifier () |
| Return the Identifier for this argument. More... | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState Static Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState | |
| static void | save_state (SavableState *s, StateOut &) |
| static SavableState * | restore_state (StateIn &si) |
| Restores objects saved with save_state. More... | |
| static SavableState * | key_restore_state (StateIn &si, const char *keyword) |
| Like restore_state, but keyword is used to override values while restoring. | |
| static SavableState * | dir_restore_state (StateIn &si, const char *objectname, const char *keyword=0) |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState | |
| SavableState (const SavableState &) | |
| SavableState (StateIn &) | |
| Each derived class StateIn CTOR handles the restore corresponding to calling save_object_state, save_vbase_state, and save_data_state listed above. More... | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount | |
| RefCount (const RefCount &) | |
| RefCount & | operator= (const RefCount &) |
 Protected Attributes inherited from sc::SimpleCo Protected Attributes inherited from sc::SimpleCo | |
| int | natoms_ |
| int * | atoms |
 Protected Attributes inherited from sc::IntCoor Protected Attributes inherited from sc::IntCoor | |
| char * | label_ |
| double | value_ |
 Static Protected Attributes inherited from sc::IntCoor Static Protected Attributes inherited from sc::IntCoor | |
| static double | bohr_conv |
| static double | radian_conv |
Detailed Description
The ScaledTorsSimpleCo class describes an scaled torsion internal coordinate of a molecule.
The scaled torsion is more stable that ordinary torsions (see the TorsSimpleCo class) in describing situations where one of the torsions plane's is given by three near linear atoms.
Designating the four atoms as 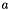 ,
, 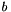 ,
, 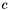 , and
, and 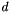 and their cartesian positions as
and their cartesian positions as 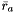 ,
, 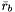 ,
, 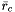 , and
, and 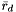 , the value of the coordinate,
, the value of the coordinate, 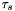 , is given by
, is given by
![\[ \bar{u}_{ab} = \frac{\bar{r}_a - \bar{r}_b}{\| \bar{r}_a - \bar{r}_b \|}\]](form_20.png)
![\[ \bar{u}_{cb} = \frac{\bar{r}_c - \bar{r}_b}{\| \bar{r}_c - \bar{r}_b \|}\]](form_21.png)
![\[ \bar{u}_{cd} = \frac{\bar{r}_c - \bar{r}_d}{\| \bar{r}_c - \bar{r}_b \|}\]](form_26.png)
![\[ \bar{n}_{abc}= \frac{\bar{u}_{ab} \times \bar{u}_{cb}} {\| \bar{u}_{ab} \times \bar{u}_{cb} \|}\]](form_32.png)
![\[ \bar{n}_{bcd}= \frac{\bar{u}_{cd} \times \bar{u}_{cb}} {\| \bar{u}_{cd} \times \bar{u}_{cb} \|}\]](form_33.png)
![\[ s = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} -1 & \mbox{if $(\bar{n}_{abc}\times\bar{n}_{bcd}) \cdot \bar{u}_{cb} > 0$} \\ 1 & \mbox{otherwise} \end{array} \right. \]](form_34.png)
![\[ \tau_s = s \sqrt{\left(1-(\bar{u}_{ab} \cdot \bar{u}_{cb}\right)^2) \left(1-(\bar{u}_{cb} \cdot \bar{u}_{cd}\right)^2)} \arccos ( - \bar{n}_{abc} \cdot \bar{n}_{bcd} )\]](form_35.png)
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ ScaledTorsSimpleCo() [1/2]
| sc::ScaledTorsSimpleCo::ScaledTorsSimpleCo | ( | const char * | refr, |
| int | , | ||
| int | , | ||
| int | , | ||
| int | |||
| ) |
This constructor takes a string containing a label, and four integers a, b, c, and d which give the indices of the atoms involved in the torsion angle abcd.
Atom numbering begins at atom 1, not atom 0.
◆ ScaledTorsSimpleCo() [2/2]
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file: