The Molecule class contains information about molecules. More...
#include <chemistry/molecule/molecule.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| Molecule (const Molecule &) | |
| Molecule (StateIn &) | |
| Molecule (const Ref< KeyVal > &input) | |
| The Molecule KeyVal constructor is used to generate a Molecule object from the input. More... | |
| Molecule & | operator= (const Molecule &) |
| void | add_atom (int Z, double x, double y, double z, const std::string &label="", double mass=0.0, int have_charge=0, double charge=0.0, int have_fragment=0, int fragment=0) |
| Add an AtomicCenter to the Molecule. | |
| const Atom & | atom (size_t i) const |
| const std::vector< Atom > & | atoms () const |
| virtual void | print (std::ostream &=ExEnv::out0()) const |
| Print information about the molecule. | |
| virtual void | print_parsedkeyval (std::ostream &=ExEnv::out0(), int print_pg=1, int print_unit=1, int number_atoms=1) const |
| Ref< Units > | geometry_units () const |
| in which units Molecule was specified and in which units it will be reported | |
| size_t | natom () const |
| Returns the number of atoms in the molecule. | |
| int | Z (int atom) const |
| double & | r (int atom, int xyz) |
| const double & | r (int atom, int xyz) const |
| const double * | r (int atom) const |
| double | mass (int atom) const |
| const char * | label (int atom) const |
| Returns the label explicitly assigned to atom. More... | |
| int | fragment (int atom) const |
| returns the fragment to which atom belongs to | |
| int | atom_at_position (double *, double tol=0.05) const |
| Takes an (x, y, z) postion and finds an atom within the given tolerance distance. More... | |
| int | atom_label_to_index (const std::string &label) const |
| Returns the index of the atom with the given label. More... | |
| std::vector< double > | charges () const |
| Returns a vector of the nuclear charges of the atoms. | |
| double | charge (int iatom) const |
| Return the charge of the atom. | |
| bool | is_Q (int iatom) const |
| Return true if iatom is a simple point charge. | |
| double | total_charge () const |
| Returns the total nuclear charge. More... | |
| int | total_Z () const |
| Returns the sum of atomic numbers of nuclei. | |
| void | set_point_group (const Ref< PointGroup > &, double tol=1.0e-7) |
| Sets the PointGroup of the molecule. | |
| const Ref< PointGroup > & | point_group () const |
| Returns the PointGroup of the molecule. | |
| Ref< PointGroup > | highest_point_group (double tol=1.0e-8) const |
| Find this molecules true point group (limited to abelian groups). More... | |
| int | is_axis (SCVector3 &origin, SCVector3 &udirection, int order, double tol=1.0e-8) const |
| Return 1 if this given axis is a symmetry element for the molecule. More... | |
| int | is_plane (SCVector3 &origin, SCVector3 &uperp, double tol=1.0e-8) const |
| Return 1 if the given plane is a symmetry element for the molecule. More... | |
| int | has_inversion (SCVector3 &origin, double tol=1.0e-8) const |
| Return 1 if the molecule has an inversion center. | |
| int | is_linear (double tolerance=1.0e-5) const |
| Returns 1 if the molecule is linear, 0 otherwise. | |
| int | is_planar (double tolerance=1.0e-5) const |
| Returns 1 if the molecule is planar, 0 otherwise. | |
| void | is_linear_planar (int &linear, int &planar, double tol=1.0e-5) const |
| Sets linear to 1 if the molecular is linear, 0 otherwise. More... | |
| SCVector3 | center_of_mass () const |
| Returns a SCVector3 containing the cartesian coordinates of the center of mass for the molecule. | |
| double | nuclear_repulsion_energy () |
| Returns the nuclear repulsion energy for the molecule. | |
| void | nuclear_repulsion_1der (int center, double xyz[3]) |
| Compute the nuclear repulsion energy first derivative with respect to the given center. | |
| void | nuclear_efield (const double *position, double *efield) |
| Compute the electric field due to the nuclei at the given point. | |
| void | nuclear_charge_efield (const double *charges, const double *position, double *efield) |
| Compute the electric field due to the given charges at the positions of the nuclei at the given point. | |
| void | symmetrize (double tol=0.5) |
| If the molecule contains only symmetry unique atoms, this function will generate the other, redundant atoms. More... | |
| void | symmetrize (const Ref< PointGroup > &pg, double tol=0.5) |
| Set the point group and then symmetrize. | |
| void | cleanup_molecule (double tol=0.1) |
| This will try to carefully correct symmetry errors in molecules. More... | |
| void | translate (const double *r) |
| void | move_to_com () |
| void | transform_to_principal_axes (int trans_frame=1) |
| void | transform_to_symmetry_frame () |
| void | print_xyz (std::ostream &=ExEnv::out0(), const char *title=0) const |
| void | principal_moments_of_inertia (double *evals, double **evecs=0) const |
| Compute the principal moments of inertia and, possibly, the principal axes. | |
| int | nunique () const |
| Return information about symmetry unique and equivalent atoms. More... | |
| int | unique (int iuniq) const |
| Returns the overall number of the iuniq'th unique atom. | |
| int | nequivalent (int iuniq) const |
| Returns the number of atoms equivalent to iuniq. | |
| int | equivalent (int iuniq, int j) const |
| Returns the j'th atom equivalent to iuniq. | |
| int | atom_to_unique (int iatom) const |
| Converts an atom number to the number of its generating unique atom. More... | |
| int | atom_to_unique_offset (int iatom) const |
| Converts an atom number to the offset of this atom in the list of generated atoms. More... | |
| int | n_core_electrons () |
| Return the number of core electrons. | |
| int | max_z () |
| Return the maximum atomic number. | |
| Ref< AtomInfo > | atominfo () const |
| Return the molecule's AtomInfo object. | |
| std::string | atom_name (int iatom) const |
| Returns the element name of the atom. | |
| std::string | atom_symbol (int iatom) const |
| Returns the element symbol of the atom. | |
| void | set_include_q (bool iq) |
| If include_q is true, then include the "Q" atoms in the charge and efield routines. | |
| bool | include_q () const |
| Returns include_q. See set_include_q. | |
| void | set_include_qq (bool iqq) |
| If include_qq is true, include the coupling between pairs of "Q" atoms when computing nuclear repulsion energy and gradients. | |
| bool | include_qq () const |
| Returns include_qq. See set_include_qq. | |
| int | n_q_atom () const |
| Retrieve the number of "Q" atoms. | |
| int | q_atom (int i) const |
| Retrieve the "Q" atoms. | |
| int | n_non_q_atom () const |
| Retrieve the number of non-"Q" atoms. | |
| int | non_q_atom (int i) const |
| Retrieve the of non-"Q" atoms. | |
| bool | any_atom_has_charge () const |
| Determine if any of the atoms have non-standard charge. | |
| bool | any_atom_has_fragment () const |
| Determine if any of the atoms have a fragment label. | |
| bool | any_atom_has_label () const |
| Determine if any of the atoms have a user defined label. | |
| SCVector3 | ref_origin () const |
| returns the origin of the reference coordinate system (the system in which atoms were specified before the center-of-mass shift | |
| void | save_data_state (StateOut &) |
| Save the base classes (with save_data_state) and the members in the same order that the StateIn CTOR initializes them. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState | |
| SavableState & | operator= (const SavableState &) |
| void | save_state (StateOut &) |
| Save the state of the object as specified by the StateOut object. More... | |
| void | save_object_state (StateOut &) |
| This can be used for saving state when the exact type of the object is known for both the save and the restore. More... | |
| virtual void | save_vbase_state (StateOut &) |
| Save the virtual bases for the object. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::DescribedClass Public Member Functions inherited from sc::DescribedClass | |
| DescribedClass (const DescribedClass &) | |
| DescribedClass & | operator= (const DescribedClass &) |
| ClassDesc * | class_desc () const MPQC__NOEXCEPT |
| This returns the unique pointer to the ClassDesc corresponding to the given type_info object. More... | |
| const char * | class_name () const |
| Return the name of the object's exact type. | |
| int | class_version () const |
| Return the version of the class. | |
| Ref< DescribedClass > | ref () |
| Return this object wrapped up in a Ref smart pointer. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount Public Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount | |
| size_t | identifier () const |
| Return the unique identifier for this object that can be compared for different objects of different types. More... | |
| int | lock_ptr () const |
| Lock this object. | |
| int | unlock_ptr () const |
| Unlock this object. | |
| void | use_locks (bool inVal) |
| start and stop using locks on this object | |
| refcount_t | nreference () const |
| Return the reference count. | |
| refcount_t | reference () |
| Increment the reference count and return the new count. | |
| refcount_t | dereference () |
| Decrement the reference count and return the new count. | |
| int | managed () const |
| void | unmanage () |
| Turn off the reference counting mechanism for this object. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | init_symmetry_info (double tol=0.5) |
| void | clear_symmetry_info () |
| void | clear () |
| void | throw_if_atom_duplicated (int begin=0, double tol=1e-3) |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState | |
| SavableState (const SavableState &) | |
| SavableState (StateIn &) | |
| Each derived class StateIn CTOR handles the restore corresponding to calling save_object_state, save_vbase_state, and save_data_state listed above. More... | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount | |
| RefCount (const RefCount &) | |
| RefCount & | operator= (const RefCount &) |
Protected Attributes | |
| std::vector< Atom > | atoms_ |
| Ref< AtomInfo > | atominfo_ |
| Ref< PointGroup > | pg_ |
| Ref< Units > | geometry_units_ |
| double | ref_origin_ [3] |
| int | nuniq_ |
| int * | nequiv_ |
| int ** | equiv_ |
| int * | atom_to_uniq_ |
| int | q_Z_ |
| bool | include_q_ |
| bool | include_qq_ |
| std::vector< int > | q_atoms_ |
| std::vector< int > | non_q_atoms_ |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState Static Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState | |
| static void | save_state (SavableState *s, StateOut &) |
| static SavableState * | restore_state (StateIn &si) |
| Restores objects saved with save_state. More... | |
| static SavableState * | key_restore_state (StateIn &si, const char *keyword) |
| Like restore_state, but keyword is used to override values while restoring. | |
| static SavableState * | dir_restore_state (StateIn &si, const char *objectname, const char *keyword=0) |
Detailed Description
The Molecule class contains information about molecules.
It has a KeyVal constructor that can create a new molecule from atomic coordinates read from a file in one of supported chemical file formats (e.g. XYZ), or from a set of keywords that give explicitly the Cartesian coordinates of the atoms.
If your version of MPQC was compiled with OpenBabel2 support, then input file can be any chemical file format understood by OpenBabel2. The following ParsedKeyVal input reads from a file in Chemical Markup Language (CML) format h2o.cml, to be interpreted by OpenBabel2:
molecule<Molecule>: ( file = "h2o.cml" )
Without OpenBabel2, only XYZ format is supported. The following ParsedKeyVal input reads from the XYZ file h2o.xyz:
molecule<Molecule>: ( xyz_file = "h2o.xyz" )
The most flexible method to specify atomic coordinates explicitly. The following input does that by using the ParsedKeyVal table notation:
molecule<Molecule>: (
unit=angstrom
{ atom_labels atoms geometry } = {
O1 O [ 0.000000000 0 0.369372944 ]
H1 H [ 0.783975899 0 -0.184686472 ]
H2 H [-0.783975899 0 -0.184686472 ]
}
)
)
The default units are Bohr which can be overridden with unit=angstrom. The atom_labels array can be omitted. The atoms and geometry arrays are required.
As a special case, an atom can be given with the symbol Q or the name charge. Such centers are treated as point charges and not given basis functions. The values of the charges must be specified with a charge vector in the Molecule input. Since the charge vector assign charges to all centers, including atoms, it is easiest to place all point charge centers first in the geometry, and then give a charge vector with a number of elements equal to the number of point charges. The following example shows a water molecule interacting with a point charge having value 0.1:
molecule<Molecule>: (
unit=angstrom
charge = [ 0.1 ]
{ atom_labels atoms geometry } = {
Q1 Q [ 0.0 0 10.0 ]
O1 O [ 0.000000000 0 0.369372944 ]
H1 H [ 0.783975899 0 -0.184686472 ]
H2 H [-0.783975899 0 -0.184686472 ]
}
)
)
This feature is designed for doing QM/MM calculations, so, by default, methods will not include interactions between the Q centers when computing the energy or the gradient. To include these interactions, set include_qq=1.
The Molecule class has a PointGroup member object, which also has a KeyVal constructor that is called when a Molecule is made. The following example constructs a molecule with 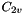 symmetry:
symmetry:
molecule<Molecule>: (
symmetry=c2v
unit=angstrom
{ atoms geometry } = {
O [0.000000000 0 0.369372944 ]
H [0.783975899 0 -0.184686472 ]
}
)
)
Only the symmetry unique atoms need to be specified. Nonunique atoms can be given too, however, numerical errors in the geometry specification can result in the generation of extra atoms so be careful.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ Molecule()
The Molecule KeyVal constructor is used to generate a Molecule object from the input.
Several examples are given in the Molecule class overview. The full list of keywords that are accepted is below.
| Keyword | Type | Default | Description |
include_q | boolean | false | Some of the atoms can be specified as |
include_qq | boolean | false | Some of the atoms can be specified as |
atominfo | AtomInfo | library values | This gives information about each atom, such as the symbol, name, and various atomic radii. |
symmetry | string | C1 | The Schoenflies symbol of the point group. This is case insensitive. It should be a subgroup of D2h. If it is |
symmetry_tolerance | double | 1.0e-4 | When a molecule has symmetry, some atoms may be related by symmetry operations. The distance between given atoms and atoms generated by symmetry operations is compared to this threshold to determine if they are the same. If they are the same, then the coordinates are cleaned up to make them exactly symmetry equivalent. If the given molecule was produced by a optimization that started in C1 symmetry, but produced a roughly symmetric structure and you would like to begin using symmetry, then this may need to be increased a bit to properly symmetrize the molecule. |
symmetry_frame | double[3][3] | [[1 0 0][0 1 0][0 0 1]] | The symmetry frame. Ignored for |
origin | double[3] | [0 0 0] | The origin of the symmetry frame. Ignored for |
redundant_atoms | boolean | false | If true, do not generate symmetry equivalent atoms; they are already given in the input. It should not be necessary to specify this option, since, by default, if a symmetry operation duplicates an atom, the generated atom will not be added to the list of atoms. Ignored for |
file | string | undefined | This gives the name of a file in one of the formats understood by OpenBabel2, from which the nuclear coordinates will be read. If this is given, the following options will be ignored. Requires OpenBabel2. |
xyz_file | string | undefined | This gives the name of a XYZ file, from which the nuclear coordinates will be read. If this is given, the following options will be ignored. |
unit | string | bohr | This gives the name of the units used for the geometry. See the Units class for information about the known units. This replaces deprecated keywords that are still recognized: |
geometry | double[][3] | none | This gives the Cartesian coordinates of the molecule. This is ignored if any of the |
atoms | string[] | none | This gives the chemical element symbol for each atom. This is ignored if any of the |
ghost | boolean[] | none | If true, the atom will be given zero charge. It will still have basis functions, however. This is used to estimate basis set superposition error. This is ignored if any of the |
charge | double[] | Z for each atom | Allows specification of the charge for each atom. This is ignored if any of the |
atom_labels | string[] | none | This gives a user defined atom label for each atom. This is ignored if any of the |
mass | double[] | Taken from AtomInfo given by the atominfo keyword. | This gives a user defined mass for each atom. This is ignored if any of the |
fragment | integer[] | none | Allows to specify fragments of Molecule. Fragment indices can be arbitrary integers and they do not be consecutive (i.e. one could specify only fragments 1 and 7). By default, all atoms belong to fragment 0. This feature is relevant only for some computations. This keyword is ignored any of the |
Member Function Documentation
◆ atom_at_position()
| int sc::Molecule::atom_at_position | ( | double * | , |
| double | tol = 0.05 |
||
| ) | const |
Takes an (x, y, z) postion and finds an atom within the given tolerance distance.
If no atom is found -1 is returned.
◆ atom_label_to_index()
| int sc::Molecule::atom_label_to_index | ( | const std::string & | label | ) | const |
Returns the index of the atom with the given label.
If the label cannot be found -1 is returned.
◆ atom_to_unique()
|
inline |
Converts an atom number to the number of its generating unique atom.
The return value is in [0, nunique).
◆ atom_to_unique_offset()
| int sc::Molecule::atom_to_unique_offset | ( | int | iatom | ) | const |
Converts an atom number to the offset of this atom in the list of generated atoms.
The unique atom itself is allows offset 0.
◆ cleanup_molecule()
| void sc::Molecule::cleanup_molecule | ( | double | tol = 0.1 | ) |
This will try to carefully correct symmetry errors in molecules.
- Exceptions
-
AlgorithmException will be thrown if any atom is out of place by more then tol
◆ highest_point_group()
| Ref<PointGroup> sc::Molecule::highest_point_group | ( | double | tol = 1.0e-8 | ) | const |
Find this molecules true point group (limited to abelian groups).
If the point group of this molecule is set to the highest point group, then the origin must first be set to the center of mass.
◆ is_axis()
| int sc::Molecule::is_axis | ( | SCVector3 & | origin, |
| SCVector3 & | udirection, | ||
| int | order, | ||
| double | tol = 1.0e-8 |
||
| ) | const |
Return 1 if this given axis is a symmetry element for the molecule.
The direction vector must be a unit vector.
◆ is_linear_planar()
| void sc::Molecule::is_linear_planar | ( | int & | linear, |
| int & | planar, | ||
| double | tol = 1.0e-5 |
||
| ) | const |
Sets linear to 1 if the molecular is linear, 0 otherwise.
Sets planar to 1 if the molecular is planar, 0 otherwise.
◆ is_plane()
Return 1 if the given plane is a symmetry element for the molecule.
The perpendicular vector must be a unit vector.
◆ label()
| const char* sc::Molecule::label | ( | int | atom | ) | const |
Returns the label explicitly assigned to atom.
If no label has been assigned, then null is returned.
◆ nunique()
|
inline |
Return information about symmetry unique and equivalent atoms.
Returns the number of symmetry-unique atoms
◆ save_data_state()
|
virtual |
Save the base classes (with save_data_state) and the members in the same order that the StateIn CTOR initializes them.
This must be implemented by the derived class if the class has data.
Reimplemented from sc::SavableState.
◆ symmetrize()
| void sc::Molecule::symmetrize | ( | double | tol = 0.5 | ) |
If the molecule contains only symmetry unique atoms, this function will generate the other, redundant atoms.
The redundant atom will only be generated if there is no other atoms within a distance of tol. If the is another atom and it is not identical, then abort will be called.
◆ total_charge()
| double sc::Molecule::total_charge | ( | ) | const |
Returns the total nuclear charge.
If include_q is true, this includes classical charges.
Referenced by mpqc::TA::Wavefunction::total_charge().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- src/lib/chemistry/molecule/molecule.h