The GaussianBasisSet class is used describe a basis set composed of atomic gaussian orbitals. More...
#include <chemistry/qc/basis/gaussbas.h>
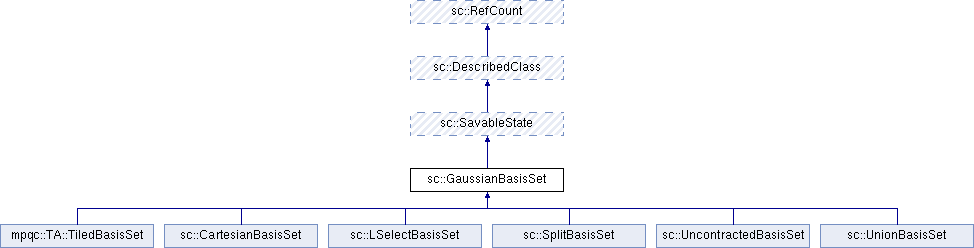
Classes | |
| class | Shell |
| Shell is a GaussianShell that is part of GaussianBasisSet, i.e. has a center on which it's centered. More... | |
| class | ValueData |
| This holds scratch data needed to compute basis function values. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| Ref< GaussianBasisSet > | operator+ (const Ref< GaussianBasisSet > &B) |
| Uses UnionBasisSet to construct the sum of this and B. More... | |
| GaussianBasisSet & | operator= (const GaussianBasisSet &A) |
| const std::string & | name () const |
| Return the name of the basis set (is nonnull only if keyword "name" was provided) | |
| const std::string & | label () const |
| Return the label of the basis set. More... | |
| Ref< Molecule > | molecule () const |
| Return the Molecule object. | |
| Ref< SCMatrixKit > | matrixkit () |
| Returns the SCMatrixKit that is to be used for AO bases. | |
| Ref< SCMatrixKit > | so_matrixkit () |
| Returns the SCMatrixKit that is to be used for SO bases. | |
| RefSCDimension | basisdim () |
| Returns the SCDimension object for the dimension. | |
| unsigned int | ncenter () const |
| Return the number of centers. | |
| unsigned int | nshell () const |
| Return the number of shells. | |
| int | nshell_on_center (int icenter) const |
| Return the number of shells on the given center. | |
| int | shell_on_center (int icenter, int shell) const |
| Return the overall shell number, given a center and the shell number on that center. More... | |
| int | shell_to_center (int ishell) const |
| Return the center on which the given shell is located. More... | |
| unsigned int | nbasis () const |
| Return the number of basis functions. | |
| unsigned int | nbasis_on_center (int icenter) const |
| Return the number of basis functions on the given center. | |
| unsigned int | nprimitive () const |
| Return the number of primitive Gaussians (sum of number of primitives for each Shell) | |
| bool | has_pure () const |
| Return true if basis contains solid harmonics Gaussians. | |
| unsigned int | max_nfunction_in_shell () const |
| Return the maximum number of functions that any shell has. | |
| unsigned int | max_ncartesian_in_shell (int aminc=0) const |
| Return the maximum number of Cartesian functions that any shell has. More... | |
| unsigned int | max_nprimitive_in_shell () const |
| Return the maximum number of primitive Gaussian that any shell has. | |
| unsigned int | max_angular_momentum () const |
| Return the highest angular momentum in any shell. | |
| unsigned int | max_ncontraction () const |
| Return the maximum number of Gaussians in a contraction in any shell. | |
| unsigned int | max_am_for_contraction (int con) const |
| Return the maximum angular momentum found in the given contraction number for any shell. More... | |
| unsigned int | max_cartesian () const |
| Return the maximum number of Cartesian functions in any shell. | |
| int | shell_to_function (int i) const |
| Return the number of the first function in the given shell. | |
| int | function_to_shell (int i) const |
| Return the shell to which the given function belongs. | |
| const Shell & | operator() (int i) const |
| Return a reference to Shell number i. | |
| Shell & | operator() (int i) |
| Return a reference to Shell number i. | |
| const Shell & | operator[] (int i) const |
| Return a reference to Shell number i. | |
| Shell & | operator[] (int i) |
| Return a reference to Shell number i. | |
| const Shell & | shell (int i) const |
| Return a reference to Shell number i. | |
| Shell & | shell (int i) |
| Return a reference to Shell number i. | |
| const Shell & | operator() (int icenter, int ishell) const |
| Return a reference to Shell number ishell on center icenter. | |
| Shell & | operator() (int icenter, int ishell) |
| Return a reference to Shell number ishell on center icenter. | |
| const Shell & | shell (int i, int j) const |
| Return a reference to Shell number j on center i. | |
| Shell & | shell (int i, int j) |
| Return a reference to Shell number j on center i. | |
| int | find (int C, const GaussianShell &S) const |
| Return the absolute index of shell S located at center C in this basis. If the shell is not found, returns -1. | |
| double | r (int icenter, int xyz) const |
| The location of center icenter. More... | |
| int | values (const SCVector3 &r, ValueData *, double *basis_values) const |
| Compute the values for this basis set at position r. More... | |
| int | grad_values (const SCVector3 &r, ValueData *, double *g_values, double *basis_values=0) const |
| Like values(...), but computes gradients of the basis function values, too. More... | |
| int | hessian_values (const SCVector3 &r, ValueData *, double *h_values, double *g_values=0, double *basis_values=0) const |
| Like values(...), but computes first and second derivatives of the basis function values, too. More... | |
| int | shell_values (const SCVector3 &r, int sh, ValueData *, double *basis_values) const |
| Compute the values for the given shell functions at position r. More... | |
| int | grad_shell_values (const SCVector3 &r, int sh, ValueData *, double *g_values, double *basis_values=0) const |
| Like values(...), but computes gradients of the shell function values, too. More... | |
| int | hessian_shell_values (const SCVector3 &r, int sh, ValueData *, double *h_values, double *g_values=0, double *basis_values=0) const |
| Like values(...), but computes first and second derivatives of the shell function values, too. More... | |
| int | equiv (const Ref< GaussianBasisSet > &b) |
| Returns true if this and the argument are equivalent. | |
| void | print_brief (std::ostream &=ExEnv::out0()) const |
| Print a brief description of the basis set. | |
| virtual void | print (std::ostream &=ExEnv::out0()) const |
| Print a detailed description of the basis set. | |
Serialization | |
| GaussianBasisSet (StateIn &si) | |
restores this from si | |
| void | save_data_state (StateOut &so) |
saves this to so | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState | |
| SavableState & | operator= (const SavableState &) |
| void | save_state (StateOut &) |
| Save the state of the object as specified by the StateOut object. More... | |
| void | save_object_state (StateOut &) |
| This can be used for saving state when the exact type of the object is known for both the save and the restore. More... | |
| virtual void | save_vbase_state (StateOut &) |
| Save the virtual bases for the object. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::DescribedClass Public Member Functions inherited from sc::DescribedClass | |
| DescribedClass (const DescribedClass &) | |
| DescribedClass & | operator= (const DescribedClass &) |
| ClassDesc * | class_desc () const MPQC__NOEXCEPT |
| This returns the unique pointer to the ClassDesc corresponding to the given type_info object. More... | |
| const char * | class_name () const |
| Return the name of the object's exact type. | |
| int | class_version () const |
| Return the version of the class. | |
| Ref< DescribedClass > | ref () |
| Return this object wrapped up in a Ref smart pointer. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount Public Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount | |
| size_t | identifier () const |
| Return the unique identifier for this object that can be compared for different objects of different types. More... | |
| int | lock_ptr () const |
| Lock this object. | |
| int | unlock_ptr () const |
| Unlock this object. | |
| void | use_locks (bool inVal) |
| start and stop using locks on this object | |
| refcount_t | nreference () const |
| Return the reference count. | |
| refcount_t | reference () |
| Increment the reference count and return the new count. | |
| refcount_t | dereference () |
| Decrement the reference count and return the new count. | |
| int | managed () const |
| void | unmanage () |
| Turn off the reference counting mechanism for this object. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | set_matrixkit (const Ref< SCMatrixKit > &) |
| void | init (std::string name, std::string label, const Ref< Molecule > &molecule, const std::vector< Shell > &shell) |
| Initializes everything. More... | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState | |
| SavableState (const SavableState &) | |
| SavableState (StateIn &) | |
| Each derived class StateIn CTOR handles the restore corresponding to calling save_object_state, save_vbase_state, and save_data_state listed above. More... | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount Protected Member Functions inherited from sc::RefCount | |
| RefCount (const RefCount &) | |
| RefCount & | operator= (const RefCount &) |
Protected Attributes | |
| Ref< Molecule > | molecule_ |
Friends | |
| class | UnionBasisSet |
Constructors | |
| GaussianBasisSet (const Ref< KeyVal > &) | |
| The KeyVal constructor. More... | |
| GaussianBasisSet (const Ref< Molecule > &molecule, const std::vector< GaussianShell > &shells, const std::vector< unsigned int > &shell_to_center, std::string name=std::string(), std::string label=std::string()) | |
| Constructs GaussianBasisSet from a Molecule and a vector of GaussianShells. More... | |
| GaussianBasisSet (const GaussianBasisSet &) | |
| static Ref< GaussianBasisSet > | unit () |
| This will produce a GaussianBasisSet object composed of a a single "unit" basis function, i.e. More... | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState Static Public Member Functions inherited from sc::SavableState | |
| static void | save_state (SavableState *s, StateOut &) |
| static SavableState * | restore_state (StateIn &si) |
| Restores objects saved with save_state. More... | |
| static SavableState * | key_restore_state (StateIn &si, const char *keyword) |
| Like restore_state, but keyword is used to override values while restoring. | |
| static SavableState * | dir_restore_state (StateIn &si, const char *objectname, const char *keyword=0) |
Detailed Description
The GaussianBasisSet class is used describe a basis set composed of atomic gaussian orbitals.
Inputs for common basis sets are included in the MPQC distribution. They have been obtained from the EMSL Basis Set Database and translated into the MPQC format. The citation for this database is below. The technical citation for each basis set is listed in the individual basis set data files, in MPQC's lib/basis directory.
Following is a table with available basis sets listing the supported elements for each basis and the number of basis functions for H, 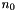 , first row,
, first row, 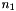 , and second row,
, and second row, 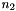 , atoms. Basis sets with non-alpha-numerical characters in their name must be given in quotes.
, atoms. Basis sets with non-alpha-numerical characters in their name must be given in quotes.
| Basis Set | Elements | 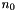 | 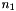 | 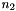 |
STO-2G | H-Ca | 1 | 5 | 9 |
STO-3G | H-Kr | 1 | 5 | 9 |
STO-3G* | H-Ar | 1 | 5 | 14 |
STO-6G | H-Kr | 1 | 5 | 9 |
MINI (Huzinaga) | H-Ca | 1 | 5 | 9 |
MINI (Scaled) | H-Ca | 1 | 5 | 9 |
MIDI (Huzinaga) | H-Na, Al-K | 2 | 9 | 13 |
DZ (Dunning) | H, Li, B-Ne, Al-Cl | 2 | 10 | 18 |
DZP (Dunning) | H, Li, B-Ne, Al-Cl | 5 | 16 | 24 |
DZP + Diffuse (Dunning) | H, B-Ne | 6 | 19 | |
3-21G | H-Kr | 2 | 9 | 13 |
3-21G* | H-Ar | 2 | 9 | 19 |
3-21++G | H-Ar | 3 | 13 | 17 |
3-21++G* | H-Ar | 3 | 13 | 23 |
4-31G | H-Ne, P-Cl | 2 | 9 | 13 |
6-31G | H-Zn | 2 | 9 | 13 |
6-31G* | H-Zn | 2 | 15 | 19 |
6-31G** | H-Zn | 5 | 15 | 19 |
6-31+G* | H-Ar | 2 | 19 | 23 |
6-31++G | H-Ca | 3 | 13 | 17 |
6-31++G* | H-Ar | 3 | 19 | 23 |
6-31++G** | H-Ar | 6 | 19 | 23 |
6-311G | H-Ca, Ga-Kr | 3 | 13 | 21 |
6-311G* | H-Ca, Ga-Kr | 3 | 18 | 26 |
6-311G** | H-Ca, Ga-Kr | 6 | 18 | 26 |
6-311G(2df,2pd) | H-Ne, K, Ca | 14 | 30 | |
6-311++G** | H-Ne | 7 | 22 | |
6-311++G(2d,2p) | H-Ca | 10 | 27 | 35 |
6-311++G(3df,3pd) | H-Ar | 18 | 39 | 47 |
cc-pVDZ | H-Ar, Ca, Ga-Kr | 5 | 14 | 18 |
cc-pVTZ | H-Ar, Ca, Ga-Kr | 14 | 30 | 34 |
cc-pVQZ | H-Ar, Ca, Ga-Kr | 30 | 55 | 59 |
cc-pV5Z | H-Ar, Ca, Ga-Kr | 55 | 91 | 95 |
cc-pV6Z | H, He, B-Ne, Al-Ar | 91 | 140 | 144 |
aug-cc-pVDZ | H, He, B-Ne, Al-Ar, Ga-Kr | 9 | 23 | 27 |
aug-cc-pVTZ | H, He, B-Ne, Al-Ar, Ga-Kr | 23 | 46 | 50 |
aug-cc-pVQZ | H, He, B-Ne, Al-Ar, Ga-Kr | 46 | 80 | 84 |
aug-cc-pV5Z | H, He, B-Ne, Al-Ar, Ga-Kr | 80 | 127 | 131 |
aug-cc-pV6Z | H, He, B-Ne, Al-Ar | 127 | 189 | 193 |
cc-pCVDZ | Li, B-Ar | 18 | 27 | |
cc-pCVTZ | Li, B-Ar | 43 | 59 | |
cc-pCVQZ | Li, B-Ar | 84 | 109 | |
cc-pCV5Z | B-Ne | 145 | ||
aug-cc-pCVDZ | B-F, Al-Ar | 27 | 36 | |
aug-cc-pCVTZ | B-Ne, Al-Ar | 59 | 75 | |
aug-cc-pCVQZ | B-Ne, Al-Ar | 109 | 134 | |
aug-cc-pCV5Z | B-F | 181 | ||
NASA Ames ANO | H, B-Ne, Al, P, Ti, Fe, Ni | 30 | 55 | 59 |
pc-0 | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 2 | 9 | 13 |
pc-1 | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 5 | 14 | 18 |
pc-2 | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 14 | 30 | 34 |
pc-3 | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 34 | 64 | 64 |
pc-4 | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 63 | 109 | 105 |
pc-0-aug | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 3 | 13 | 17 |
pc-1-aug | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 9 | 23 | 27 |
pc-2-aug | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 23 | 46 | 50 |
pc-3-aug | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 50 | 89 | 89 |
pc-4-aug | H, C-F, Si-Cl | 88 | 145 | 141 |
All basis sets were obtained from the Extensible Computational Chemistry Environment Basis Set Database, Version 12/03/03, as developed and distributed by the Molecular Science Computing Facility, Environmental and Molecular Sciences Laboratory which is part of the Pacific Northwest Laboratory, P.O. Box 999, Richland, Washington 99352, USA, and funded by the U.S. Department of Energy. The Pacific Northwest Laboratory is a multi-program laboratory operated by Battelle Memorial Institute for the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC06-76RLO 1830. Contact David Feller or Karen Schuchardt for further information.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ GaussianBasisSet() [1/2]
The KeyVal constructor.
moleculeThe gives a Molecule object. The is no default.
pureamIf this boolean parameter is true then 5D, 7F, etc. will be used. Otherwise all cartesian functions will be used. The default depends on the particular basis set.
nameThis is a string giving the name of the basis set. The above table of basis sets gives some of the recognized basis set names. It may be necessary to put the name in double quotes. There is no default.
basisIf the
elementvector is given, then this vector specifies the names of basis sets for each element. If theelementvector is not given, this vector specifies basis set name for each atom in the molecule (note that the same basis name must be specified for each set of atoms related by symmetry). If this keyword omitted, the basis set specified innamewill be used for all atoms.elementThis is a vector of elements. If it is given then it must have the same number of entries as the basis vector.
basisdirA string giving a directory where basis set data files are to be sought. See the text below for a complete description of what directories are consulted.
basisfilesEach keyword in this vector of files is appended to the directory specified with basisdir and basis set data is read from them.
Several files in various directories are checked for basis set data. First, basis sets can be given by the user in the basis section at the top level of the main input file. Next, if a path is given with the basisdir keyword, then all of the files given with the basisfiles keyword are read in after appending their names to the value of basisdir. Basis sets can be given in these files in the basis section at the top level as well. If the named basis set still cannot be found, then GaussianBasisSet will try convert the basis set name to a file name (see the note below for the rules of this conversion) and check first in the directory given by basisdir. Next it checks for the environment variable MPQC_DATA_PATH. If it is set it will look for the basis file in $MPQC_DATA_PATH/basis. Otherwise it will look in the source code distribution in the directory SC/lib/basis. If the executable has changed machines or the source code has be moved, then it may be necessary to copy the library files to your machine and set the MPQC_DATA_PATH environmental variable.
Note: translation of a basis name to a file name will convert upper-case letters(A-Z) to the lower-case letters, characters ',' and ' ' (whitespace) to '_', character '+' to 'P', character '*' to 'S', character '(' to 'L', and character ')' to 'R'.
The basis set itself is also given in the ParsedKeyVal format. There are two recognized formats for basis sets:
- array of shells
One must specify the keyword :basis: followed by the lowercase atomic name followed by : followed by the basis set name (which may need to be placed inside double quotes). The value for the keyword is an array of shells. Each shell reads the following keywords:
typeThis is a vector that describes each component of this shell. For each element the following two keywords are read:
amThe angular momentum of the component. This can be given as the letter designation, s, p, d, etc. There is no default.
pureamIf this boolean parameter is true then 5D, 7F, etc. shells are used. The default is false. This parameter can be overridden in the GaussianBasisSet specification.
expThis is a vector giving the exponents of the primitive Gaussian functions.
coefThis is a matrix giving the coeffients of the primitive Gaussian functions. The first index gives the component number of the shell and the second gives the primitive number.
An example might be easier to understand. This is a basis set specificition for STO-2G carbon:
basis: ( carbon: "STO-2G": [ (type: [(am = s)] { exp coef:0 } = { 27.38503303 0.43012850 4.87452205 0.67891353 }) (type: [(am = p) (am = s)] { exp coef:1 coef:0 } = { 1.13674819 0.04947177 0.51154071 0.28830936 0.96378241 0.61281990 }) ] )- basis set of even-tempered primitive Gaussians
Such basis set format is given as a group of keywords. The name of the group is :basis: followed by the lowercase atomic name followed by : followed by the basis set name (which may need to be placed inside double quotes). The group of keywords must contain vectors
amandnprim, which specify the angular momentum and the number of shells in each block of even-tempered primitives. In addition, one must provide any two of the following vectors:first_expThe exponent of the "tightest" primitive Gaussian in the block.
last_expThe exponent of the most "diffuse" primitive Gaussian in the block.
exp_ratioThe ratio of exponents of consecutive primitive Gaussians in the block.
Note that the dimensions of each vector must be the same.
Here's an example of a basis set composed of 2 blocks of even-tempered s-functions and 1 block of even-tempered p-functions.
basis: ( neon: "20s5s13p":(
am = [ 0 0 1 ] nprim = [ 20 5 13 ] first_exp = [ 1000.0 0.1 70.0 ] last_exp = [ 1.0 0.01 0.1 ]
) )
◆ GaussianBasisSet() [2/2]
| sc::GaussianBasisSet::GaussianBasisSet | ( | const Ref< Molecule > & | molecule, |
| const std::vector< GaussianShell > & | shells, | ||
| const std::vector< unsigned int > & | shell_to_center, | ||
| std::string | name = std::string(), |
||
| std::string | label = std::string() |
||
| ) |
Constructs GaussianBasisSet from a Molecule and a vector of GaussianShells.
- Parameters
-
molecule molecule whose centers will serve as origins for shellsshells vector of GaussianShell objects shell_to_center maps shell -> center; shells on the same center MUST appear in succession name label
Member Function Documentation
◆ grad_shell_values()
| int sc::GaussianBasisSet::grad_shell_values | ( | const SCVector3 & | r, |
| int | sh, | ||
| ValueData * | , | ||
| double * | g_values, | ||
| double * | basis_values = 0 |
||
| ) | const |
Like values(...), but computes gradients of the shell function values, too.
See the other grad_values(...) members for more information.
◆ grad_values()
| int sc::GaussianBasisSet::grad_values | ( | const SCVector3 & | r, |
| ValueData * | , | ||
| double * | g_values, | ||
| double * | basis_values = 0 |
||
| ) | const |
Like values(...), but computes gradients of the basis function values, too.
The g_values argument must be vector of length 3*nbasis. The data will be written in the order bf1_x, bf1_y, bf1_z, ...
◆ hessian_shell_values()
| int sc::GaussianBasisSet::hessian_shell_values | ( | const SCVector3 & | r, |
| int | sh, | ||
| ValueData * | , | ||
| double * | h_values, | ||
| double * | g_values = 0, |
||
| double * | basis_values = 0 |
||
| ) | const |
Like values(...), but computes first and second derivatives of the shell function values, too.
See the other hessian_values(...) members for more information.
◆ hessian_values()
| int sc::GaussianBasisSet::hessian_values | ( | const SCVector3 & | r, |
| ValueData * | , | ||
| double * | h_values, | ||
| double * | g_values = 0, |
||
| double * | basis_values = 0 |
||
| ) | const |
Like values(...), but computes first and second derivatives of the basis function values, too.
h_values must be vector of length 6*nbasis. The data will be written in the order bf1_xx, bf1_yx, bf1_yy, bf1_zx, bf1_zy, bf1_zz, ...
◆ init()
|
protected |
Initializes everything.
To be used by derived classes.
◆ label()
|
inline |
◆ max_am_for_contraction()
| unsigned int sc::GaussianBasisSet::max_am_for_contraction | ( | int | con | ) | const |
Return the maximum angular momentum found in the given contraction number for any shell.
◆ max_ncartesian_in_shell()
| unsigned int sc::GaussianBasisSet::max_ncartesian_in_shell | ( | int | aminc = 0 | ) | const |
Return the maximum number of Cartesian functions that any shell has.
The optional argument is an angular momentum increment.
◆ operator+()
| Ref<GaussianBasisSet> sc::GaussianBasisSet::operator+ | ( | const Ref< GaussianBasisSet > & | B | ) |
Uses UnionBasisSet to construct the sum of this and B.
◆ r()
| double sc::GaussianBasisSet::r | ( | int | icenter, |
| int | xyz | ||
| ) | const |
The location of center icenter.
The xyz argument is 0 for x, 1 for y, and 2 for z.
◆ shell_on_center()
| int sc::GaussianBasisSet::shell_on_center | ( | int | icenter, |
| int | shell | ||
| ) | const |
Return the overall shell number, given a center and the shell number on that center.
Shells on the same center have consecutive indices.
- See also
- shell_to_center()
◆ shell_to_center()
|
inline |
Return the center on which the given shell is located.
- Note
- There are no guarantees about shell->center map, other than the shells on the same center are be consecutive.
◆ shell_values()
| int sc::GaussianBasisSet::shell_values | ( | const SCVector3 & | r, |
| int | sh, | ||
| ValueData * | , | ||
| double * | basis_values | ||
| ) | const |
Compute the values for the given shell functions at position r.
See the other values(...) members for more information.
◆ unit()
|
static |
This will produce a GaussianBasisSet object composed of a a single "unit" basis function, i.e.
that is one everywhere. This can be used with integral evaluators to compute certain classes of integrals, with limitations.
◆ values()
Compute the values for this basis set at position r.
The basis_values argument must be vector of length nbasis.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- src/lib/chemistry/qc/basis/gaussbas.h